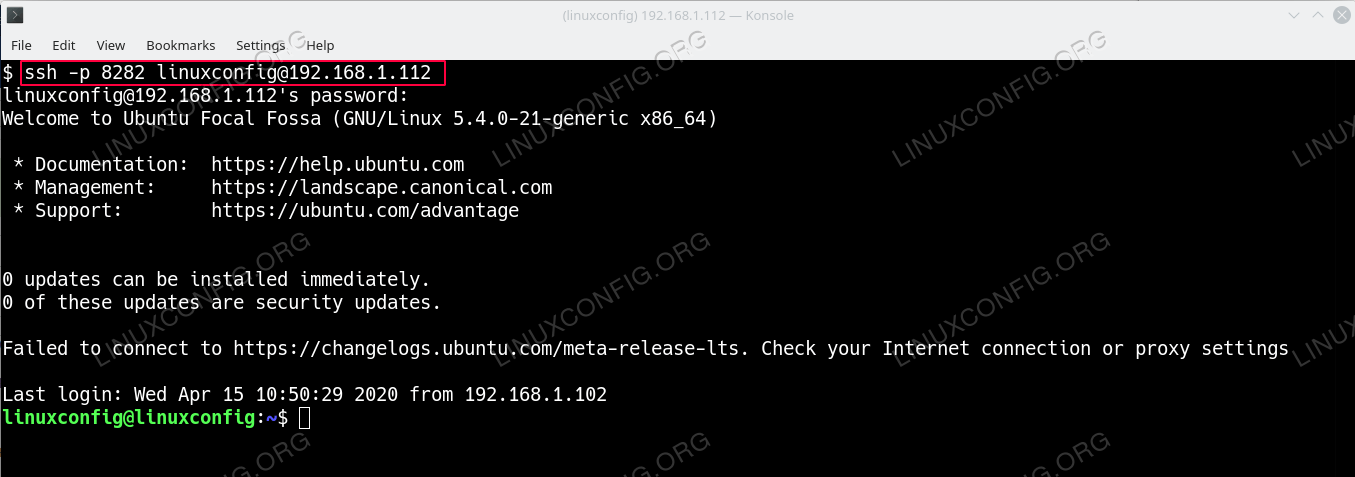
OpenSSH servers run by default TCP port 22. We call it generally ssh port. Ssh portnumber is know for the whole world so attackers can attack to beat our OpenSSHserver like brute forcing. Get Ssh Server Port Number From Ssh Configuration. SSH server by default listens to port 22 and you don't have to manually specify the port number on your SSH client if you're connecting to the default port. You'll have to manually specify the port number when you're connecting to non-standard SSH ports using the -p option or by adding the port information in your SSH client's configuration file. Remote SSH port forwarding is commonly used by employees to open backdoors into the enterprise. For example, the employee may set get a free-tier server from Amazon AWS, and log in from the office to that server, specifying remote forwarding from a port on the server to some server or application on the internal enterprise network. Enter the hostname or IP address and port number of the destination SSH server on the main PuTTY Sessions screen. Use the Category list to navigate to Connection SSH Tunnels. Select Dynamic to define the type of SSH port forward. Enter the dynamic port number in the Source port field (e.g., 5534).
Applies to Windows Server 2019, Windows 10
OpenSSH is a connectivity tool for remote login that uses the SSH protocol. It encrypts all traffic between client and server to eliminate eavesdropping, connection hijacking, and other attacks.
OpenSSH can be used to connect Window 10 clients to Windows Server 2019. OpenSSH Client is available to install on Windows 10 build 1809 and later, while OpenSSH Server is available to install on Windows Server 2019 and later.
Important
If you downloaded OpenSSH from the GitHub repo at PowerShell/openssh-portable, follow the instructions listed there, not the ones in this article.
Install OpenSSH using Windows Settings

Both OpenSSH components can be installed using Windows Settings. OpenSSH Server is installed on Windows Server and OpenSSH Client is installed on Windows 10 devices.
To install the OpenSSH components:
Open Settings, select Apps > Apps & Features, then select Optional Features.
Scan the list to see if the OpenSSH is already installed. If not, at the top of the page, select Add a feature, then:
- On Windows 10, find OpenSSH Client, then click Install
- On Windows Server 2019, find OpenSSH Server, then click Install
Ssh Server Port
Once setup completes, return to Apps > Apps & Features and Optional Features and you should see OpenSSH listed.
Change Openssh Port Windows
Note
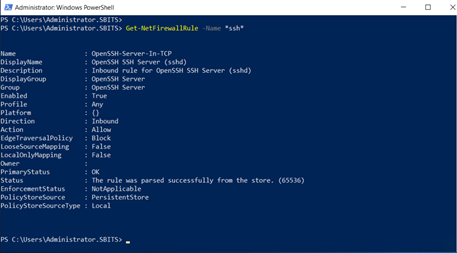
Installing OpenSSH Server will create and enable a firewall rule named OpenSSH-Server-In-TCP. This allows inbound SSH traffic on port 22. If this rule is not enabled and this port is not open, connections will be refused or reset.
Install OpenSSH using PowerShell
To install OpenSSH using PowerShell, run PowerShell as an Administrator.To make sure that OpenSSH is available, run the following cmdlet:
This should return the following output:
Windows Openssh Server Port Forward
Then, install the server or client components as needed:
Both of these should return the following output:

Openssh Server Portal
Start and configure SSH Server
To start and configure OpenSSH server for initial use, open PowerShell as an administrator, then run the following commands to start the SSHD service:
Connect to SSH Server
Once installed, you can connect to OpenSSH Server from a Windows 10 device with the SSH client installed using PowerShell as follows. Be sure to run PowerShell as an administrator:
Once connected, you get a message similar to the following:
Selecting yes adds that server to the list of known ssh hosts on your Windows client.
You are prompted for the password at this point. As a security precaution, your password will not be displayed as you type.
Once connected, you will see the Windows command shell prompt:
Uninstall OpenSSH using Windows Settings
To uninstall OpenSSH using Windows Settings:
- Open Settings, then go to Apps > Apps & Features.
- Go to Optional Features.
- In the list, select OpenSSH Client or OpenSSH Server.
- Select Uninstall.
Uninstall OpenSSH using PowerShell
To uninstall the OpenSSH components using PowerShell, use the following commands:
You may need to restart Windows afterwards if the service was in use at the time it was uninstalled.
