Multifocal atrial tachycardia (MAT) is a rapid heart rate. It occurs when too many signals (electrical impulses) are sent from the upper heart (atria) to the lower heart (ventricles).
When you ask such questions you need to give more information. Age (sex), weight height, diagnoses, activity, when it happens, how long it lasts, how long you have it per episode and that kind of info. Keep a record lke that for the doctor. Tachycardia refers to a heart rate that’s too fast. How that’s defined may depend on your age and physical condition. Generally speaking, for adults, a heart rate of more than 100 beats per minute (BPM) is considered too fast. View an animation of tachycardia. A normal resting heart rate for adults ranges from 60 to 100 beats per minute. Generally, a lower heart rate at rest implies more efficient heart function and better cardiovascular fitness. For example, a well-trained athlete might have a normal resting heart rate. A pulse oximeter to check your oxygen saturation level and your heart rate at home. 9 hours ago Bayern Munich chairman Karl-Heinz Rummenigge believes plans for the Super League are 'definitively over', a week after the short-lived attempt by 12.
The human heart gives off electrical impulses, or signals, which tell it to beat. Normally, these signals begin in an area of the upper right chamber called the sinoatrial node (sinus node or SA node). This node is considered the heart's 'natural pacemaker.' It helps control the heartbeat. When the heart detects a signal, it contracts (or beats).
The normal heart rate in adults is about 60 to 100 beats per minute. The normal heart rate is faster in children.
In MAT, many locations in the atria fire signals at the same time. Too many signals lead to a rapid heart rate. It most often ranges between 100 to 130 beats per minute or more in adults. The rapid heart rate causes the heart to work too hard and not move blood efficiently. If the heartbeat is very fast, there is less time for the heart chamber to fill with blood between beats. Therefore, not enough blood is pumped to the brain and the rest of the body with each contraction.
MAT is most common in people age 50 and over. It is often seen in people with conditions that lower the amount of oxygen in the blood. These conditions include:
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Lung failure
You may be at higher risk for MAT if you have:
- Had surgery within the last 6 weeks
- Overdosed on the drug theophylline
- Sepsis
When the heart rate is less than 100 beats per minute, the arrhythmia is called 'wandering atrial pacemaker.'
Some people may have no symptoms. When symptoms occur, they can include:
- Chest tightness
- Sensation of feeling the heart is beating irregularly or too fast (palpitations)
- Weight loss and failure to thrive in infants
Other symptoms that can occur with this disease:
A physical exam shows a fast irregular heartbeat of over 100 beats per minute. Blood pressure is normal or low. There may be signs of poor circulation.
Pulse Over 100 Not Always Sinus Tachycardia
Tests to diagnose MAT include:
- Electrophysiologic study (EPS)
Heart monitors are used to record the rapid heartbeat. These include:
- 24-hour Holter monitor
- Portable, long-term loop recorders that allow you to start recording if symptoms occur
If you are in the hospital, your heart rhythm will be monitored 24 hours a day, at least at first.
If you have a condition that can lead to MAT, that condition should be treated first.

Treatment for MAT includes:
- Improving blood oxygen levels
- Giving magnesium or potassium through a vein
- Stopping medicines, such as theophylline, which can increase heart rate
- Taking medicines to slow the heart rate (if the heart rate is too fast), such as calcium channel blockers (verapamil, diltiazem) or beta-blockers
MAT can be controlled if the condition that causes the rapid heartbeat is treated and controlled.
Complications may include:
- Reduced pumping action of the heart
What If Your Pulse Is Over 100
Adobe lightroom cc mac download. Call your health care provider if:
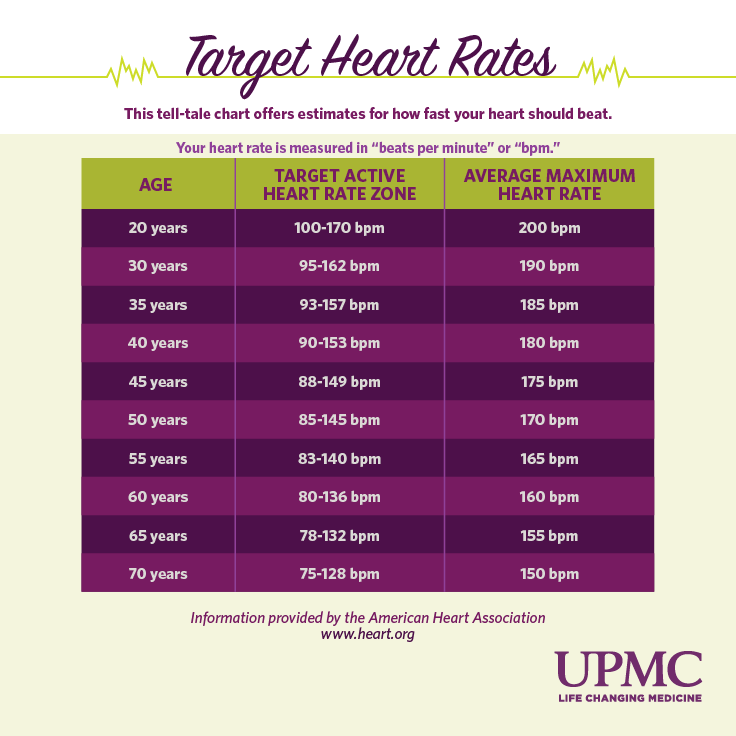
- You have a rapid or irregular heartbeat with other MAT symptoms
- You have MAT and your symptoms get worse, do not improve with treatment, or you develop new symptoms
To reduce the risk of developing MAT, treat the disorders that cause it right away.
Pulse Over 100

Olgin JE, Zipes DP. Supraventricular arrhythmias. In: Zipes DP, Libby P, Bonow RO, Mann DL, Tomaselli GF, Braunwald E, eds. Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 37.
Pulse Over 100 Covid
Zimetbaum P. Supraventricular cardiac arrhythmias. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 58.
Pulse Over 100 At Rest
Updated by: Micaela Iantorno, MD, MSc, FAHA, RPVI, Interventional Cardiologist at Mary Washington Hospital Center, Fredericksburg, VA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
