- Human Pulse Locations In Body
- Pedal Pulse Assessment Scale
- Human Pulse Sounds
- Human Pulse Locations
- Human Pulse Rate 132

“The Human Rights Pulse’s writer’s workshop served as the right kind of embellishment I was looking for, to improve my writing skills. The workshop provided me with an opportunity to align my ideas and writing style in a way to serve the readers with concise and cohort matter. The American Heart Association states the normal resting adult human heart rate is 60–100 bpm. Tachycardia is a high heart rate, defined as above 100 bpm at rest. Bradycardia is a low heart rate, defined as below 60 bpm at rest. During sleep a slow heartbeat with rates around 40–50 bpm is common and is considered normal.
Learn how to check pulse points in this nursing assessment review.
We will review 9 common pulse points on the human body. As a nurse you will be assessing many of these pulse points regularly, while others you will only assess at certain times.
When you assess a pulse point you will be assessing:
- Rate: count the pulse rate for 30 seconds and multiply by 2 if the pulse rate is regular, OR 1 full minute if the pulse rate is irregular.
- Always count the apical pulse for 1 full minute.
- A normal pulse rate in an adult is 60-100 bpm.
- Strength: grade the strength of the pulse and check the pulse points bilaterally and compare them. NOTE: always check the carotid pulse points individually (not at the same time) to avoid stimulating the vagal response.
- 0: absent
- 1+: weak
- 2+: normal
- 3+: bounding
- Rhythm: is the pulse regular or irregular
9 Common Pulse Points (start from head-to-toe…this makes it easier when you have to perform this skill)
- Temporal
- Carotid
- Apical
- Brachial
- Radial
- Femoral
- Popliteal
- Posterior Tibial
- Dorsalis Pedis
Pulse Points Demonstration
Temporal
This artery comes off of the external carotid artery and is found in front of the tragus and above the zygomatic arch (cheekbone). This pulse point is assessed during the head-to-toe assessment of the head.
Carotid
This site is most commonly used during CPR in an adult as a pulse check site. It is a major artery that supplies the neck, face, and brain. As noted above, palpate one side at a time to prevent triggering the vagus nerve, which will decrease the heart rate and circulation to the brain.
To find the carotid pulse point, tilt the head to the side and palpate below the jaw line between the trachea and sternomastoid muscle.
Apical
This site is assessed during the head-to-toe assessment and before the administration of Digoxin. The pulse rate should be 60 bpm or greater in an adult before the administration of Digoxin. Always count the pulse rate for 1 full minute with your stethoscope at this location.
The apical pulse is the point of maximal impulse and is found at the apex of the heart. It is located on the left side of the chest at the 5th intercostal space midclavicular line.
To find the pulse point:
- Locate the sternal notch
- Palpate down the Angle of Louis
- Find the 2nd intercostal space on the left side of the chest
- Go to the 5th intercostal space at the midclavicular line and this is the apical pulse point
Brachial
This is a major artery in the upper arm that divides into the radial and ulnar artery. This site is used to measure blood pressure and as a pulse check site on an infant during CPR.
To find this pulse point, extend the arm and have the palms facing upward. The pulse point is found near the top of the cubital fossa, which is a triangular area that is in front of the elbow.
Radial
This is a major artery in the lower arm that comes off of the brachial artery. It provides circulation to the arm and hand. It is most commonly used as the site to count a heart rate in an adult.
Copytrans manager mac os x download. To find this pulse point, extend the arm out and have the palms facing upward. It is found below the thumb in the wrist area along the radial bone.
Femoral
This is a major artery found in the groin and it provides circulation to the legs. This artery is palpated deeply in the groin below the inguinal ligament between the pubic symphysis and anterior superior iliac spine.
Popliteal
This artery is found behind the knee and comes off of the femoral artery. It is a rather deep artery like the femoral.


To find the artery, the knee should be flexed. It is located near the middle of the popliteal fossa, which is a diamond-shaped pitted area behind the knee. Use two hands to palpate the artery…one hand assisting to flex the knee and the other to palpate the artery.
Posterior Tibial
Human Pulse Locations In Body
This pulse point, along with the dorsal pedis, is assessed during the head-to-toe assessment and is particularly important in patients who have peripheral vascular disease or a vascular procedure (example: heart catheterization when the femoral artery was used to assess the heart).
The posterior tibial pulse point is found on the inside of the ankle between the medial malleolus (bony part of the ankle bone) and Achilles tendon.
Dorsalis Pedis
To find this artery, locate the EHL (extensor hallucis longus) tendon by having the patient extend the big toe. Then palpate down this tendon and when you come to end of it, go to the side of the tendon and you will find this pulse point.

Overview
What is your pulse?
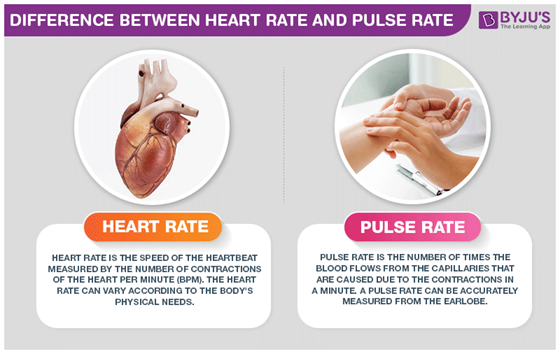
Your pulse is your heart rate, or the number of times your heart beats in one minute. Pulse rates vary from person to person. Your pulse is lower when you are at rest and increases when you exercise (more oxygen-rich blood is needed by the body when you exercise). Knowing how to take your pulse can help you evaluate your exercise program.
How to take your pulse
- Place the tips of your index, second and third fingers on the palm side of your other wrist below the base of the thumb. Or, place the tips of your index and second fingers on your lower neck on either side of your windpipe.
- Press lightly with your fingers until you feel the blood pulsing beneath your fingers. You may need to move your fingers around slightly up or down until you feel the pulsing.
- Use a watch with a second hand, or look at a clock with a second hand.
- Count the beats you feel for 10 seconds. Multiply this number by six to get your heart rate (pulse) per minute.
Pedal Pulse Assessment Scale
Count your pulse: _____ beats in 10 seconds x 6 = _____ beats/minute
What is a normal pulse?
Normal heart rates at rest:
- Children (ages 6 - 15) 70 – 100 beats per minute
- Adults (age 18 and over) 60 – 100 beats per minute
Test Details
What is maximum heart rate?
The maximum heart rate is the highest heart rate achieved during maximal exercise. One simple method to calculate your predicted maximum heart rate, uses this formula:
220 - your age = predicted maximum heart rate
Example: a 40-year-old's predicted maximum heart rate is 180 beats/minute.
There are other formulas that take into account the variations in maximal heart rate with age and gender. If you are interested in learning more about these more accurate but slightly more complicated formulas please see these resources:
- Gellish RL, Goslin BR, Olson RE, McDonald A, Russi GD, Moudgil VK. Longitudinal modeling of the relationship between age and maximal heart rate. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2007 May;39(5):822-9. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17468581
- Gulati M, Shaw LJ, Thisted RA, Black HR, Bairey Merz CN, Arnsdorf MF. Heart rate response to exercise stress testing in asymptomatic women: the st. James women take heart project. Circulation. 2010 Jul 13;122(2):130-7. Epub 2010 Jun 28. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20585008
Your actual maximum heart rate is most accurately determined by a medically supervised maximal graded exercise test.
Please note that some medications and medical conditions may affect your heart rate. If you are taking medications or have a medical condition (such as heart disease, high blood pressure or diabetes), always ask your doctor if your maximum heart rate/target heart rate will be affected. If so, your heart rate ranges for exercise should be prescribed by your doctor or an exercise specialist.
What is target heart rate?
- You gain the most benefits and lessen the risks when you exercise in your target heart rate zone. Usually this is when your exercise heart rate (pulse) is 60 to 80% of your maximum heart rate. In some cases, your health care provider may decrease your target heart rate zone to begin with 50% .
- In some cases, High Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) may be beneficial. This should be discussed with a healthcare professional before beginning. With HIIT exercise, heart rates zones may exceed 85%.
- Always check with your healthcare provider before starting an exercise program. Your provider can help you find a program and target heart rate zone that matches your needs, goals and physical condition.
- When beginning an exercise program, you may need to gradually build up to a level that's within your target heart rate zone, especially if you haven't exercised regularly before. If the exercise feels too hard, slow down. You will reduce your risk of injury and enjoy the exercise more if you don't try to over-do it!
- To find out if you are exercising in your target zone (between 60 and 80% of your maximum heart rate), stop exercising and check your 10-second pulse. If your pulse is below your target zone (see below), increase your rate of exercise. If your pulse is above your target zone, decrease your rate of exercise.
What is your target zone?
Target Heart Rate Zones by Age *
Human Pulse Sounds
- Age: 20
- Target Heart Rate (HR) Zone (60-85%): ** 120 – 170
- Predicted Maximum HR: 200
- Age: 25
- Target Heart Rate (HR) Zone (60-85%): 117 – 166
- Predicted Maximum HR: 195
- Age: 30
- Target Heart Rate (HR) Zone (60-85%): 114 – 162
- Predicted Maximum HR: 190
- Age:35
- Target Heart Rate (HR) Zone (60-85%): ** 111 – 157
- Predicted Maximum HR: 185
- Age: 40
- Target Heart Rate (HR) Zone (60-85%): 108 – 153
- Predicted Maximum HR: 180
- Age: 45
- Target Heart Rate (HR) Zone (60-85%): 105 – 149
- Predicted Maximum HR: 175
- Age: 50
- Target Heart Rate (HR) Zone (60-85%): 102 – 145
- Predicted Maximum HR: 170
- Age:55
- Target Heart Rate (HR) Zone (60-85%): 99 – 140
- Predicted Maximum HR: 165
- Age:60
- Target Heart Rate (HR) Zone (60-85%): 96 – 136
- Predicted Maximum HR: 160
- Age:65
- Target Heart Rate (HR) Zone (60-85%): 93 – 132
- Predicted Maximum HR: 155
- Age:70
- Target Heart Rate (HR) Zone (60-85%): 90 – 123
- Predicted Maximum HR: 150
Your Actual Values (Actual Values are determined from a graded exercise test)
- Target HR
- Max. HR
Human Pulse Locations
* This chart is based on the formula: 220 - your age = predicted maximum heart rate.
Resources
Human Pulse Rate 132
For more information about exercise
- Exercise for Your Heart Health.
- Exercise: Make Your Program a Success.
- To make an appointment with an exercise specialist or to join a cardiac rehabilitation program, contact the Cleveland Clinic Preventive Cardiology and Rehabilitation Program at 216.444.9353 or 800.223.2273, ext. 9353
- To find a cardiac rehabilitation program in your area, contact the American Association of Cardiopulmonary Rehabilitation.
- American Heart Association.
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute.
